What is the Meaning of Insurance?
Insurance is a contract between two parties where one party called ‘the insurer’ undertakes in exchange for a fixed sum called ‘premium’ to pay the other party called ‘the insured’, a fixed amount of money on the happening of a certain event. When such a contract is complete it is known as a ‘policy’.
Below that well will learn about the kinds of insurance.
Life Insurance Policies
Life insurance is a contract providing for payment of a sum of money to the person assured or failing him, to the person entitled to receive the same, on the happening of certain events. The life insurance corporation came into existence with the objective of assurance of:
- Family protection
- Provision for old age
- Tax concession
- Housing loans
- Loans advanced for educational purposes
- Donations to charitable institutions. To meet the above-said objectives, various types of life insurance policies are being issued by the Life Insurance Corporation of India
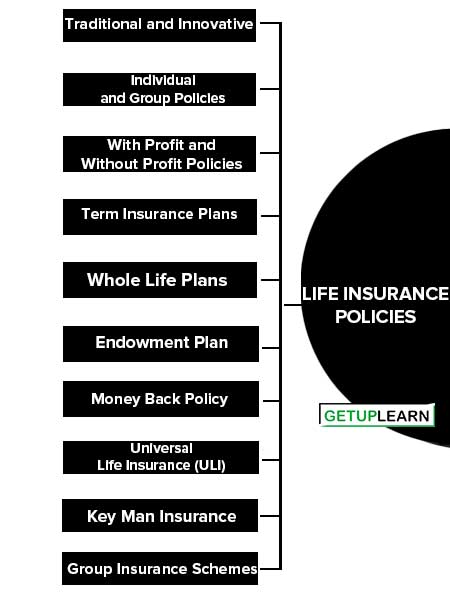
Classification of Life Insurance Policies
Life Insurance policies can be classified into the following types:
- Traditional and Innovative
- Individual and Group Policies
- With Profit and Without Profit Policies
- Term Insurance Plans
- Whole Life Plans
- Endowment Plan
- Money Back Policy
- Universal Life Insurance (ULI)
- Key Man Insurance
- Group Insurance Schemes
Traditional and Innovative
These policies provide benefits of risk coverage with or without savings to the insured. Such policies have been in existence for a long and the terms and conditions of such policies and quite inflexible, as they do not come with section copy assurance, whole–life, endowment, or money-back policies.
Non-traditional policies are new-age products. They offer innovative plans, which are designed to suit different types of persons often combined with various options to offer flexibility and choice to buyers of insurance.
Individual and Group Policies
Individual policies cater to the need of a single person and his family members. Group policies provide insurance coverage to a group of related persons.
With Profit and Without Profit Policies
They are participating in policies in which the policyholder is entitled to participate in the profits. Which is determined through the periodical valuation of assets and liabilities as per statutory requirements. The surplus is usually distributed in the form of a bonus, declared after such a valuation, and is paid at the time of final settlement.
These plans are popular in India because the majority purchase life insurance policies for the purpose of savings. Without profit policies, the insured will not have any share of interest in the share of the surplus of the insurer. They are meant for the coverage of risk. The rate of premium is lower for these policies than that of “with profit plans”.
Term Insurance Plans
In the term insurance plans the insurer promises the insured to pay the face value mentioned in the policy in case the insured does premature. These are short-term policies. They are subjected to renewal without evidence of insurability at each term. The period of coverage starts from one year onwards.
Whole Life Plans
These policies remain valid as long as the policyholder is alive.
Features of Whole Life Plans:
- Covers risk for the entire lifetime.
- Claims can be made only after the death of the insured.
- Loans can be availed when the policy acquired surrender value.
- Premiums are higher than term insurance policies.
- The minimum age required is 18 and the maximum is 6 years.
- The premium amount to be paid is the same throughout.
- The insured cannot claim the money during the lifetime of the policyholders.
- The minimum age of entry is 18 years and the maximum age is 60 years.
- The policy is also available with payment of premiums limited to a certain pre-determined number of years.
Endowment Plan
Endowment refers to the accumulated value of the investment made under the policy. Thus, Endowment plans promise protection from risk in the event of the death of the insured during the policy term as well as an assured sum upon the maturity of the policy.
In this type of policy, the maturity of the policy is usually chosen to coincide with the retirement of the person. The policy of the term varies from 10 to 30 years. In case of short duration, the premium involved is higher.
Features of Endowment Plan:
It covers the risk for a prescribed time period at the expiry of which the sum under the policy, along with the accumulated bonus is paid back to the assured.
- The payment of an endowment at the end of the term has made these policies popular in our country.
- It provides old-age benefits.
- Its premiums are higher and bonus rates are lower when compared to the whole-life- policies.
- They are eligible for loans within the surrender value of the policy.
- They can be issued up to the age of 65 years, the maximum age at maturity being 75 years.
Money Back Policy
In this case, the policy proceeds are paid to the insured in a number of separate cash payments. The receipt of payments can be as per the available option. Insurance cover is provided sent life in other types.
Features of Money Back Policy:
- In case of death, the entire sum assured is paid without deducting any survival benefit amounts already paid.
- In the case of survival, the sum assured after deducting the survival benefit amount is paid with a bonus.
- The minimum age limit is 12 years.
Universal Life Insurance (ULI)
These are innovative in nature. These are familiar in the U.S. They suit the present-day market dynamics. The policyholder can take advantage of the flexibility offered and can act as per the market changes taking place. It is evolved due to the disadvantages of traditional life insurance policies.
Features of Universal Life Insurance (ULI):
The premium paid is divided into two parts. One part covers the risk of life and the other part accounts for savings which is invested in high-yielding securities. The frequency of premium payment is flexible. The policyholder can pay according to his financial convenience. It provides guaranteed returns.
Key Man Insurance
It is insurance taken by a company on the life of an important employee – a key – man of the company – against financial loss that may occur from the employee’s premature death.
Under this plan, a key man (KM) can be an expert, a Technocrat, a Director, a shareholder, and an Executive. The key man may be defined as an employee whose death would result in a financial loss to the company.
Group Insurance Schemes
LIC offers life insurance protection under group policies to various groups such as employer – employees, professional co-operatives, weaker sections of society, etc. It also provides insurance coverage to people under certain approved occupations at subsidized rates under social security group schemes.
Besides providing insurance coverage which provides funding for gratuity and pension liabilities of the employers.
Kinds of Insurance
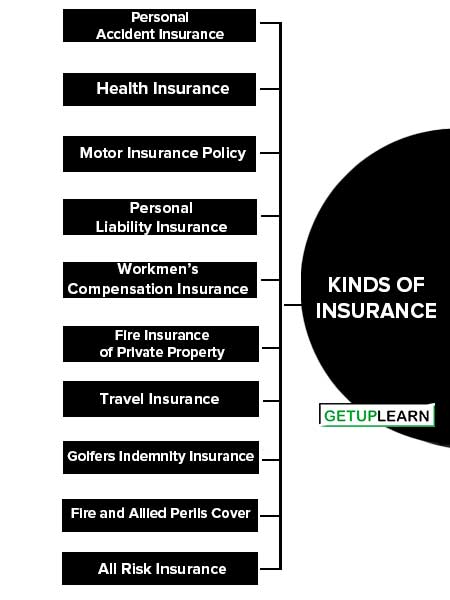
These are important kinds of insurance:
- Personal Accident Insurance
- Health Insurance
- Motor Insurance Policy
- Personal Liability Insurance
- Workmen’s Compensation Insurance
- Fire Insurance of Private Property
- Travel Insurance
- Golfers Indemnity Insurance
- Fire and Allied Perils Cover
- All Risk Insurance
- Machinery Insurance Policy
- Boiler and Pressure Plants
- Burglary Insurance for Business
- Product Liability Insurance
- Professional Indemnity Insurance
- Marine Insurance
- Crime Insurance
Personal Insurance
Section 6B of the Insurance Act, of 1938 defines general insurance. It means fire, marine, or miscellaneous insurance business whether carried on single or in combination with one or more of them. Nonlife insurance products are otherwise called general insurance products.
They are broadly classified as fire, marine (cargo and hull), and miscellaneous (motor, health, liability, personal accident property, rural, engineering, workmen compensation, aviation, and crop). Nearly 175 products are under general insurance for the public sector insurance companies but the new players have fewer products. The policies under the general insurance business are of two types:
- Health Insurance
- Motor Insurance Policy
- Personal Liability Insurance
- Workmen’s Compensation Insurance
- Fire Insurance of Private Property
- Travel Insurance
- Golfers Indemnity Insurance
Personal Accident Insurance
It provides financial protection to the insured, provided he is insured in an accident only. The accident may result in death, total disablement, or partial disablement. Every one of us is exposed to this type of risk. The risk of accidents causes a lot of insecurity. This feeling of insecurity will have a number of repercussions on us.
To protect from the risk of accidents, General Insurance provides a number of personal accident policies to the public. It covers even certain groups like students, NRIs, Women, etc. In 1980 a new clause is added to the personal accident tariff namely the education fund.
The new clause provides additional compensation to the children of the insured for their education in case of death or permanent total disablement of the insured. It covers a number of perils. It is left to the option of the insured to take cover for one or all of the risks.
Health Insurance
It covers the financial loss arising out of poor health conditions or due to permanent disability which results in loss of income. i. A plan to meet the medical expenses is very essential due to the rise in healthcare costs. It is a very section copy of hospitalization.
In the US nearly 47% of health care expenses are met by the government through various medical benefit schemes. 19% of the expenditure is taken care of by own resources and 35% of health care expenses come from private insurance companies. Some of the health insurance policies available in India are:
- Mediclaim Policy.
- Overseas Mediclaim Policy.
- Raj Rajeswari Mahila Kalyan Yojana.
- Bhagyashree Child Welfare Policy.
- Cancer Insurance Policy.
- Jan Arogya Bima Policy etc.
It is still in the developing stage in India. The high cost of medical care is likely to contribute to its development in India. It is not recognized as a separate segment in the Indian insurance industry. Privatization of the insurance industry is likely to encourage the development of Health Insurance in the country. It has to go a long way still in India.
Motor Insurance Policy
In India, it is classified as miscellaneous. It comes under the tariff category. Persons driving cars may cause injuries to other persons. Sometimes, the insurer may cause financial loss. Similarly, the owners of all motor cars are also exposed to certain other risks. These include damage to the vehicle due to accidents, collisions, theft, fire, and so on.
The Motor Vehicle Act came into force in 1939 in India. Compulsory insurance is introduced by the Act to protect pedestrians and third parties. Claims for damages may arise due to possession of the car, usage, and maintenance of the car. Motor Insurance policy covers the financial loss arising out of these risks to the insured.
It is a contract between the insured and the insurer where the insurer promises to indemnify the financial liability in the event of loss to the insured. The Act classified Motor vehicles as private cars, motorcycles, and commercial vehicles. All India Motor Tariff applies to the motor insurance business in India. The claim settlement is made in India by replacement of payment of repair charges.
Personal Liability Insurance
It provides protection against legal liability, which arises due to the personal acts of the insured. The insurance company will pay for legal deference to third-party damages to the extent of the policy hunt. Except for legal liability, which arises due to automobile accidents and personal liability, most other personal acts are covered under personal liability insurance.
In this type, the insurance company will defend the insured in case the matter goes to a Court of law. The matters can also be settled out of court by the mutual consent of the parties involved. It offers very wide coverage.
Workmen’s Compensation Insurance
An employee is exposed to the risk of job-related accidents to his workers. According to Workmen’s Compensation Act, 1923 the employer is liable to pay compensation. In case of death and disablement (total and partial) involved in a work-related accident. Under the Act, the employer is required to pay compensation to his workers who are insured during the employment period.
He may also be liable for third-party injuries caused by an accident irrespective of whether the person is a workman or a third party. The insurer covers the employer’s liability. In India, the National Insurance Company Ltd., United India Insurance Company Ltd., Oriented Insurance Company Ltd., and the New India Assurance Company Ltd. Offer Workmen’s Compensation Policies. The Act does not cover the following: Any accident caused due to War, invasion, etc.
- A person who is not a workman under the Act.
- Removal of safety guards intentionally.
- Accidents caused due to consumption of alcohol etc.
Fire Insurance of Private Property
It is next to personal accident and health insurance. The property and also all the contents inside are exposed to risk due to fire. Fire insurance comes under the tariff class of business. All India Fire Tariff is the revised fire insurance tariff, which came into force in the year 2001.
Fire Insurance is a contract between an insurer and the insured in which the insurer will indemnify the insured against all losses arising out of perils as mentioned in the fire policies. It covers loss caused due to, fire, lighting property damage, explosion, damage due to storms, damage due to storms, damage due to bush fire, damage due to riots, strikes, and so on.
Travel Insurance
it covers travel-related accidents also, while traveling outside India, individuals face risks such as loss of baggage, accidents involving injuries, and illnesses that required hospitalization treatment. In India, it is gaining importance among international travelers and their insurance requirements are met by the nationalized insurance companies as well we the new entrants into the General Insurance industry. The coverage includes:
- Flight Life insurance, covering only single flights and travel accidents.
- Lost baggage insurance.
- Overseas health insurance.
- Trip cancellation and interruption insurance etc.
Golfers Indemnity Insurance
It provides protection against losses or damages to the gold players and to golf equipment. It also provides protection against public liability resulting in death or disability. All golf players or sports persons can insure themselves under a golfer insurance policy in order to protect their rights and interests as sports persons.
Business Insurance
Personal general insurance is a fast-growing sector in India. It’s share of contribution in more as far as business is concerned. The income from this sector is low as the risk involved is also lost when compared to commercial general insurance. The risk involved in business insurance is high. It can be offset partly by re-insurance.
So, the return on business insurance is high. The financial institutions that provide funds to companies insist on relevant business insurance. The following are some of the types of business insurance:
- Fire and Allied Perils Cover
- All Risk Insurance
- Machinery Insurance Policy
- Boiler and Pressure Plants
- Burglary Insurance for Business
- Product Liability Insurance
- Professional Indemnity Insurance
- Marine Insurance
- Crime Insurance
Fire and Allied Perils Cover
It provides coverage against damages arising from fire. It makes good the loss arising due to fire. Thus, it brings the business of the insured to normal. To claim compensation under fire insurance, the following conditions are to be satisfied.
- There must be actual ignition (presence of flames).
- The ignition must be incidental and not deliberate.
No compensation is paid if the fire occurs due to its own fermentation, damage caused due to heating, theft, etc.
All Risk Insurance
There are only two types of property and liability insurance policies. i.e. named perils policies, that cover only those perils that are mentioned in the policy and all risk policies which cover all losses except those excluded in the policy. All risk insurance includes industrial all risk insurance, contractors all risk insurance, and erection all risk insurance.
Machinery Insurance Policy
One of the 4 Ms essential for production is machinery. Production comes to a standstill if there is any machinery breakdown. Therefore, it is very essential to keep the machinery running and get it repaired at the earliest in case of a breakdown. Repairs may involve huge expenditures. It cannot be delayed.
These two essentials require the companies to avail machinery insurance coverage. The policy covers all the costs involved in putting the machinery in a normal position suitable for the production process. The producer need not maintain a reserve for the unforeseen breakdown of machinery and can invest this amount elsewhere more productively. It covers almost all the stationary capital equipment.
Boiler and Pressure Plants
This covers the loss or damage to steam-generating equipment like boilers and other fired and un-fired pressure vessels against the risk of explosion and collapse due to internal pressures that are inherent in all such equipment.
It covers damage caused due to their own explosion. Accidents in generators cannot be avoided totally even under proper care. Hence, a prudent businessman will always opt for such policies.
Burglary Insurance for Business
This type of cover is essential for business. When its property is mortgaged with any financial institution, the concerned institution will insist on this section copy type. It covers stock-in-trade; Goods held in trust, Fixtures and fittings, Plant and Machinery, etc.
It does not burglary cover theft larceny, robbery etc, as the main characteristic of burglary is forceful entry. Next line Ex: If there is cash in the safe and is insured the safe should be locked and the keys should not be anywhere near the safe.
Product Liability Insurance
Liability arises out of the fort, statutory law, or out of contract. The risk of insurance does not end with production. It is a continuous process even after production. Thus, if any third party is insured due to the insured product, the producer will be liable to pay damages.
Product liability insurance covers the damages arising in such cases. The damages payable in such cases is high. Hence, all industries that are exposed to such risks should go for this policy even though it is not mandatory.
Professional Indemnity Insurance
The counterpart of product liability insurance in the service industry is professional indemnity insurance. As product liability gives protection against the liabilities arising due to the product, professional indemnity insurance covers the professionals against all liabilities that may arise due to negligence or failure in providing service.
That is why it is called Errors and Omission Insurance or malpractice insurance. It is an important cover. It benefits not only the physicians and surgeons but also clients. Due to the liability involved the surgeons may not dare to treat the patients under critical treatment.
In other words, in its absence, the doctor would not be available when he is required most. Of late, this cover is gaining momentum and is accommodating the other professionals also.
Marine Insurance
It is the oldest form of insurance. When the Rhodesian merchants introduced the respondentia and bottomry loans in the marine trade based on the uncertainty involved, respondentia loans are loans given to the captain of the ship against the cargo to ensure the safety of the journey.
The loans are repaid only when the cargo reached the destination safely. On the other hand bottomry loans are raised against the vessels. High premiums are charged. They are almost similar to present-day marine cargo and hull insurance. Marine Insurance started for the first time in Italy in the 12th Century. From there it spread to the U.K.
- The Ship.
- Insurable goods and property.
- Third-party liabilities incurred by the insurer.
- Expenses incurred to minimize loss
Crime Insurance
Crime is one that all countries of the world are making hectic efforts to eliminate. But they are not successful. It is unfortunate to mention that the insurance companies are not making the required attention in this direction.
The U.S. insured nearly 10% of the crime loss as per the available statistics. There are two types of financial protection that are available against the losses caused by crime. They are fidelity and surety bonds and burglary, robbery, and theft insurance. Bonds and insurance are almost similar.
For example: If a building contractor is asked to deposit a bond by the owner of any building, it means the surety will pay the damages in case the contractor is not able to complete the project. Hence, to a great extent, bonds sound like insurance. Yet it is not insurance.
Fidelity bonds deal with the assurance of bonafide behavior by an employee during the course of his employment. The word itself suggests that the surety assures the employer of the trustworthiness and honesty of the employee and agrees to pay the damages that arise due to the dishonest acts of that employee.
FAQs Related to the Kinds of Insurance
What are the kinds of insurance?
These are the kinds of insurance:
1. Personal Accident Insurance
2. Health Insurance
3. Motor Insurance Policy
4. Personal Liability Insurance
5. Workmen’s Compensation Insurance
6. Fire Insurance of Private Property
7. Travel Insurance
8. Golfers Indemnity Insurance
9. Fire and Allied Perils Cover
10. All Risk Insurance.
