What is Life Insurance?
Life insurance may be defined as a contract in which the insurer in consideration of a certain premium either in lump sum or other periodical payments, agrees to pay to the assured or to the person for whose benefits the policy is taken, a stated sum of money on the happening of a particular event contingent on the duration of human life.
Thus, under a whole life Assurance, the policy money is payable at the death of the assured, and under an endowment policy, the money is payable on the assured’s surviving a stated period of years, for example, on his attaining the age of 55 or his death, should that occur earlier.
Definition of Life Insurance
These are the definitions of life insurance by the authors:
The life insurance contract embodies an agreement in which broadly stated, the insurer undertakes to pay a stipulated sum upon the death of the insured, or at some designated time to a designated beneficiary.
J.H. Magee
Life Insurance contract may be defined whereby the insurer, in consideration of a premium paid either in lumpsum or in periodical installments, undertakes to pay an annuity or a certain sum of money either on the death of the nsured or ion the expiry of a certain number of years.
R.S. Sharma
A contract of Life Assurance is that in which one partly agrees to pay a given sum on the happening of a particular event contingent upon the duration of human life in consideration of the immediate payment of a smaller sum or certain equivalent periodical payments by another.
Bunyon’s Law of Life Insurance
Meaning of Life Insurance
According to Sec. (2)(11) of the Insurance Act, Life Insurance business means “the business affecting contracts upon human life
- Any contract whereby the payment of money is assured upon death (except death by accident only) or the happening of any contingency dependent on human life.
- Any contract which is subject to the payment of premiums for a term dependent on human life.
- Any contract which includes the granting of disability and double or triple indemnity, accident benefits, the granting of annuities upon human life, and the granting of superannuation allowances.
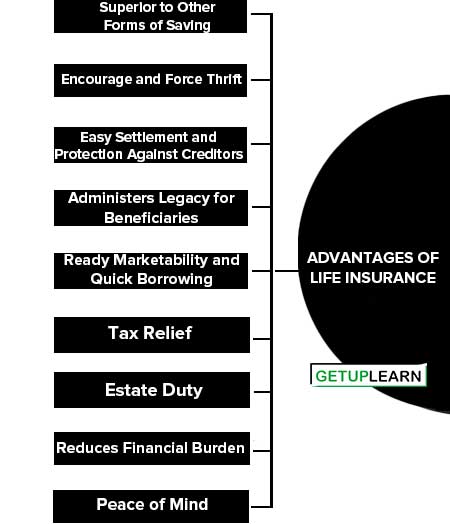
Advantages of Life Insurance
These are some important advantages of life insurance given below:
- Superior to Other Forms of Saving
- Encourage and Force Thrift
- Easy Settlement and Protection Against Creditors
- Administers Legacy for Beneficiaries
- Ready Marketability and Quick Borrowing
- Tax Relief
- Estate Duty
- Reduces Financial Burden
- Peace of Mind
Superior to Other Forms of Saving
Life insurance is superior to other forms of savings because, unlike other savings plans, it affords full protection against the risk of death. In case of death, the full sum assured is made available under a life assurance policy, whereas under other savings schemes, the total accumulated saving alone will be available.
Any saving is less than the sum assured if death occurs during the early years. It does not serve the purpose that a life assurance policy is intended to serve.
Encourage and Force Thrift
Most people do not have the willpower to continue a long-term saving plan. As savings can be easily withdrawn many may not be able to resist the temptation of using it for some less worthy purpose, which may appear important at the moment. Life Insurance provides compulsory savings.
Easy Settlement and Protection Against Creditors
The proceeds of life insurance can be used against the claims of creditors. A policy taken under the Married Women’s Property Act for the benefit of one’s wife and children is fully protected from creditors except to the extent of any interest in the policy retained by the insured. It constitutes a trust in favor of the wife/children for which no separate assignment is necessary.
Administers Legacy for Beneficiaries
As per the terms and conditions of settlement options, the corporation enables the insured to safeguard the proceeds of a policy in the interest of the beneficiaries. It happens that a provision that a husband or father has made through insurance is quickly lost through speculative or unwise investment or unnecessary expenditure on luxuries.
These contingencies can be provided against in the case of insurance as the policy-holder can arrange that in the event of his death the beneficiaries should receive a specified lump sum or payment in equal installments selected by the insured.
Ready Marketability and Quick Borrowing
If the policyholder finds himself unable to continue payment of premiums after a specific period he can surrender the policy for a cash amount. Alternatively, he can tide over the temporary difficulty by taking a loan on the policy without delay. A life insurance policy is also acceptable as security for a commercial loan.
Tax Relief
The Income Tax Act allows the deduction of a certain portion of taxable income of individuals or Hindu undivided families for computing Income tax which is diverted to payment of life insurance premiums. Taking this tax relief into account the assured is in effect paying a lower premium for his insurance.
Estate Duty
Life insurance is the most practicable way to ensure definite payment on one’s death without having to resort to the conversion of realizable assets at a loss. It affords a very satisfactory means of making provision for payment of Estate duty.
Reduces Financial Burden
Life Insurance reduces financial burden by providing for the education of children, the marriage of a daughter, building a house, or starting an adventure after retirement.
Peace of Mind
Life insurance reduces fears about the future and provides peace of mind and freedom from worries to the policyholders. In the event of premature death, the dependents get financial support from Life Insurance Corporation.
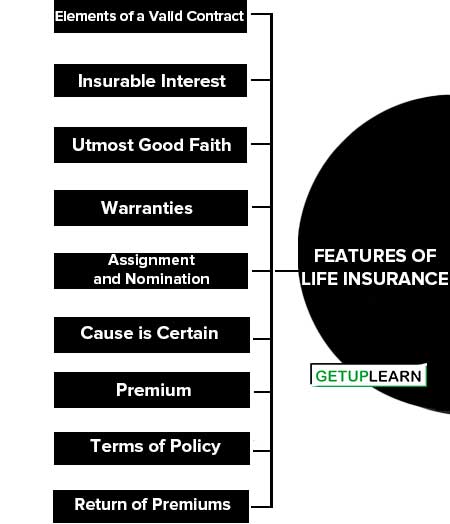
Features of Life Insurance
The following are the essential features of life insurance:
- Elements of a Valid Contract
- Insurable Interest
- Utmost Good Faith
- Warranties
- Assignment and Nomination
- Cause is Certain
- Premium
- Terms of Policy
- Return of Premiums
Elements of a Valid Contract
Contract of life insurance has the essential elements of a general contract, since the life insurance contract is a contract, as defined in the Indian Contract Act.
A valid contract of life insurance comes into existence where the essential elements of agreement (offer and acceptance, competency of the parties, free consent of the parties, legal consideration and legal objectives) are present.
Insurable Interest
A person cannot insure the life of another unless he has an insurable interest in it. The risk against this policy is the death of the insured. A person has an unlimited insurable interest in his own life.
A husband is presumed to have an insurable interest in his wife’s life and vice versa. A survey has an insurable interest in the life of the principal debtor to the extent of his claim. In life insurance, the insurable interest must exist at the time of the contract of insurance.
Utmost Good Faith
Insurance contracts, however, are contracts uberrimae fidei i.e., one based on utmost good faith or the contract of utmost good faith. The insurance is bound to disclose all the material facts and figures known to him but unknown to the insurer. Every fact that is likely to influence the mind of the insurer in deciding whether to accept the proposal or fix the rate of premium is material for this purpose.
Similarly, the insurer is bound to exercise the same good faith in disclosing, the scope of insurance which he prepared to grant. In life insurance, age income education, occupation, health family size, etc. are some examples of material facts that should be disclosed at the time of entering into the contract.
Warranties
Warranties are an important feature of the life insurance contract. Warranties are the basis of the contract between the proposer and the insurer. If any statement, whether of material or non-material facts and figures is untrue the contract shall be null and void the premium paid by him may be forfeited by the insurer.
The policy insured will contain that proposer and the personal statement shall form part of the policy and be the basis of the contract.
Assignment and Nomination
Both the assignment and nomination are essential features of the life insurance policy. Assignment of a life policy means transferring the rights of the assured in respect of the policyholder to the assignee. In the case of the nomination, a person is merely named to collect the amount to be paid by the insurer on the death of the assured.
Cause is Certain
In a life assurance policy, the insurer has to pay the insured amount one day or another because the death of the assured or his reaching a particular age is certain to happen.
Premium
The premium is the price for the risk of loss undertaken by the insurer. In the case of insurance, the premium is usually required to be paid in cash, and advance payment of the premium is a condition precedent to the creation of a binding contract of insurance.
The amount of premium for payment of the insured is paid monthly or in annual installments for a certain period. In life insurance, the premium is calculated on the average rate of mortality and the fixed periodical premium may continue either until death or for a specified number of years. Premium is payable till the maturity of the policy.
Terms of Policy
An insurance policy specifies the terms and conditions or period of time, it covers often the nature of risk against which insurance is sought, and determines the period of life of the policy. A life insurance policy may cover a specified number of years or the balance of the insured life.
Return of Premiums
Premium is the consideration for the risk run by the insurers, and if the risk insured against is not run, then consideration fails, the policy does not attach, and as a consequence, the premium paid can be recovered from the insurer.
The general principle applicable to the claim for the return of the premium is that if the insurers have never been the risk, they cannot be said to have earned the premium. But where the insurance is avoided by the insurers on the ground of breach of warranty the premium can only be recovered if it is shown there was a breach ab initial.
Life Insurance was carried on by private insurance’s before 1956; but since January 19, 1956, the Life business came under the control and ownership of the Government. In June 1956, a bill was passed for establishing the Life Insurance Corporation of India, which started functioning on September 1, 1956.
The Corporation is a body corporate having perpetual succession and a Common seal with powers to acquire, hold and dispose of property and may his name sue and be sued. There will be no more than 15 members including a Chairman thereof. The corporation is charged with the main duty to carry on the life insurance business. It has one Central Office, 7 Zonal Offices, and several divisional and Branch offices.
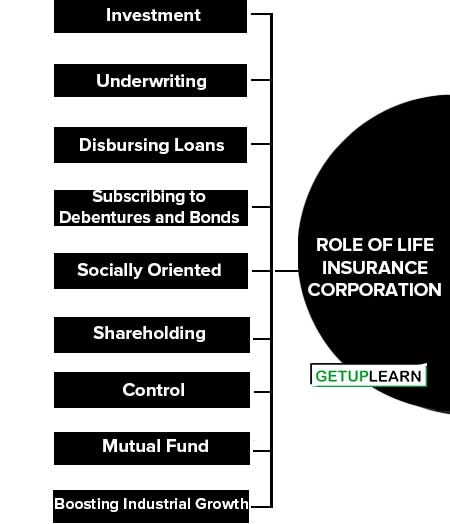
Role of Life Insurance Corporation
The role of Life Insurance Corporation involves all the activities related to the national economy, individuals, and society. The following are the important role of life insurance corporation:
- Investment
- Underwriting
- Disbursing Loans
- Subscribing to Debentures and Bonds
- Socially Oriented
- Shareholding
- Control
- Mutual Fund
- Boosting Industrial Growth
- Claims and Settlement
Investment
Life Insurance Corporation is acting as a capital market intermediary. It provides long-term investments in Government Securities, the Public sector, the Cooperative sector, the Private sector, and Joint Sector. On the Stock Exchange, it is considered a very powerful security holder.
Underwriting
LIC has been the largest underwriter of capital issues in the India capital market till the year 1978 after which it reduced its activities in favor of socially oriented projects. During the year 1983 onwards. LIC underwrites firms and prefers large and established companies.
It also prefers further issues. As an underwriter, it influences the capital market considerably and is also able to stabilize the market during the downswing or depression periods.
Disbursing Loans
Since 1970 LIC has disbursed loans for industrial development. One of the major avenues of investment in every year constituted financing through loans.
It has given loans for the generation and transmission of electricity for agriculture and industrial use, housing schemes, piped water supply schemes, and development and road and transport. Out of the total disbursement of all financial institutions to the industry, LIC’s contribution comes to around 8%.
Subscribing to Debentures and Bonds
Financial institutions and corporate enterprises requiring burgeoning funds to meet their expanding needs find it easier and cheaper to raise funds from the market by issuing commercial papers.
LIC also subscribes to debentures and bonds of various financial institutions and development banks like IDBI and IFCI. In 1983. LIC subscribed to the Debentures of ICICI of the value of rs.8 crores.
Socially Oriented
A basic feature of financial liberalization and many innovations are the trend toward social orientation. LIC has resorted to socially oriented schemes in has big way since 1978. This has brought down its activities in the capital market. The rationale behind this change has been to go in for developmental work.
Own your House (OYH) schemes have been given priority. Apart from these schemes, loans for sewerage, road and transport, and electricity generation have also been given priority in recent years.
Shareholding
By virtue of its shareholding, LIC has been recognized among the top ten shareholders in one of every three companies listed in the stock exchange on which it has share hold in companies. While LIC has invested in large blocks of equities and in later years in debenture holdings, it had kept away and did not interfere in the decisions of the management in the past.
Control
In recent years, LIC has influenced the management to take proper decisions and to tone up the quality of work in the companies financed by it. This is intended to promote confidence in the minds of the public and to exercise control in the corporate sector which often has a very small shareholding.
In 1984 LIC dominated the Indian industry scene. These changes in the direction of the LIC are bound to exert some pressure on the industry and change the complexion of the Indian industrial scenario.
Mutual Fund
It has set up in 1989, as a Mutual fund for operating various schemes for the mobilization of savings from the public particularly from the rural and urban areas, and channeling these funds to the capital market. The LIC has considerable expertise in investment management by virtue of its earlier operations of funds.
Boosting Industrial Growth
The corporation helps boost industrial growth in the country. It helps small-scale and medium-scale industries by granting loans for setting up cooperative industrial estates and an amount of rs.45 cores has so far been advanced to industrial estates and industrial development corporations.
The corporation also makes investments in the corporate sector in the form of long, medium, and short-term loans to companies/corporations.
The total investment made by way of loans up to the year 2001 was rs.2812 crores and by way of subscription to shares/debentures was rs.35048 crores. All this makes a distinct contribution towards growth in industrialization and the generation of skilled and unskilled employment opportunities in the country.
Claims and Settlement
The settlement of claims constitutes one of the important functions of the corporation. Indeed, the payment of claims may be regarded as the primary service of insurance to the public. Proper settlement of claims will be provided on the basis of a sound knowledge of law, principles, and practices governing, insurance contracts, terms and conditions of standard policies, etc.
FAQs Related to the Life Insurance
What is the meaning of life insurance?
A contract of Life Assurance is that in which one partly agrees to pay a given sum on the happening of a particular event contingent upon the duration of human life in consideration of the immediate payment of a smaller sum or certain equivalent periodical payments by another.
What is the simple definition of life insurance?
The life insurance contract embodies an agreement in which broadly stated, the insurer undertakes to pay a stipulated sum upon the death of the insured, or at some designated time to a designated beneficiary. By J.H. Magee
What are the advantages of life insurance?
The advantages of life insurance are:
1. Superior to Other Forms of Saving
2. Encourage and Force Thrift
3. Easy Settlement and Protection Against Creditors
4. Administers Legacy for Beneficiaries
5. Ready Marketability and Quick Borrowing
6. Tax Relief
7. Estate Duty
8. Reduces Financial Burden
9. Peace of Mind.
What is the role of Life Insurance Corporation?
These are the role of life insurance corporation:
1. Investment
2. Underwriting
3. Disbursing Loans
4. Subscribing to Debentures and Bonds
5. Socially Oriented
6. Shareholding
7. Control
8. Mutual Fund
9. Boosting Industrial Growth
10. Claims and Settlement.
