What is a System Concept?
The term “System” is derived from the Greek word system. It means an organized relationship among functional units or components. We can define a System as a combination of resources or functional units working together to accomplish a given task.
The term “working together” in the system definition is very important as all the components are interrelated and interdependent and cannot exist independently. As the definition says, these components interact with each other to accomplish a given task, which is actually the objective of the system.
The components that comprise a system may be the various inputs required by the system, the outcomes or the outputs of the system, the resources required to make the system functional, etc. Below that we will be learning deeply about System Concepts.
Characteristics of System Concepts
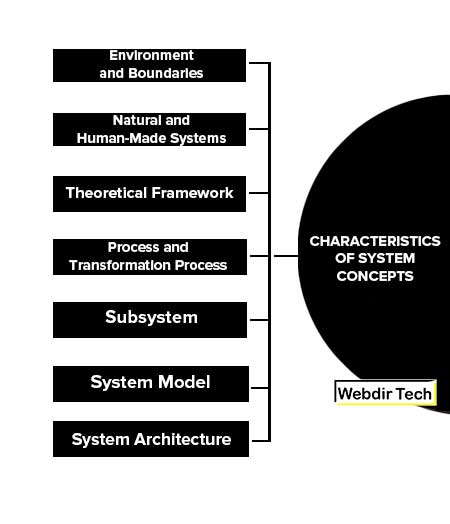
These are the characteristics of system concepts included in the system concept:
- Environment and Boundaries
- Natural and Human-Made Systems
- Theoretical Framework
- Process and Transformation Process
- Subsystem
- System Model
- System Architecture
- Environment and Boundaries
Systems are considered complex systems of interconnected parts. System defining its boundary; this means choosing which entities are inside the system and which are outside – part of the environment.
We then make simplified representations (models) of the system to understand it and predict or impact its future behavior. These models may define the structure and/or the behavior of the system.
Natural and Human-Made Systems
There are natural and human-made (designed) systems. Natural systems may not have an apparent objective but their outputs can be interpreted as purposes. Human-made systems are made with purposes that are achieved by the delivery of outputs. Their parts must be related; they must be “designed to work as a coherent entity” else they would be two or more distinct systems.
Theoretical Framework
An open system exchanges matter and energy with its surroundings. Most systems are open systems; like a car, coffeemakers, or computers. A closed system exchanges energy, but not matter, with its environment; like Earth. An isolated system exchanges neither matter nor energy with its environment. A theoretical example of such a system is the Universe.
Process and Transformation Process
A system can also be viewed as a bounded transformation process, that is, a process or collection of processes that transform inputs and outputs. Inputs are consumed; outputs are produced. The concept of input and output here is very broad. Eg., the output of a passenger ship is the movement of people from departure to destination.
Subsystem
A subsystem is a set of elements, which is a system itself, and components of a larger system.
System Model
A system comprises multiple views. For man-made systems, it may be such views as planning, requirements (analysis), design, implementation, deployment, structure, behavior, input data, and output data views. A systems model is a requirement to describe and represent all these multiple views.
System Architecture
A system architecture, using one single integrated model for the description of multiple views such as planning, the requirement (analysis), design, implementation, deployment, structure, behavior, input data, and output data views, is a kind of systems model.
Definition of System
Below that we have explained the definition of system as easier as possible:
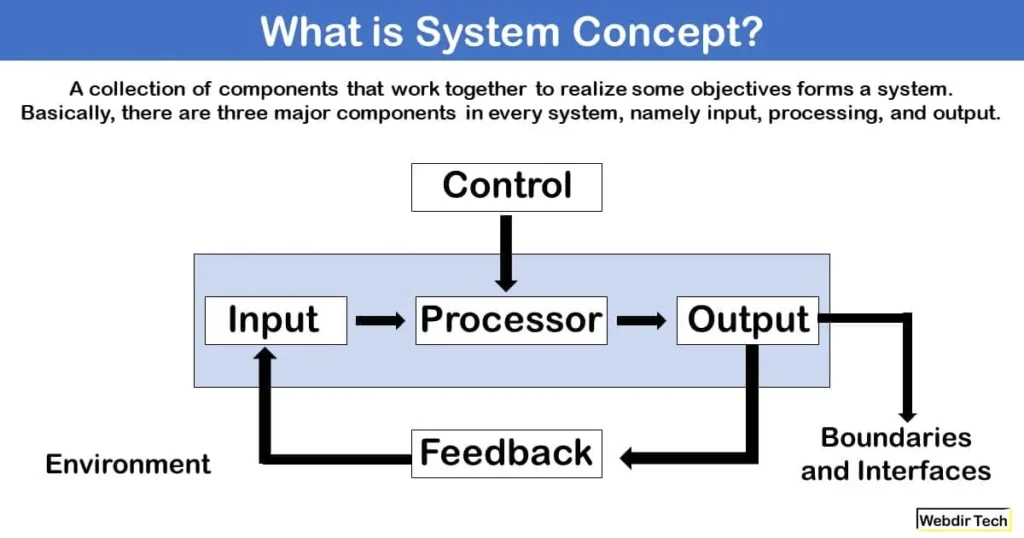
A collection of components that work together to realize some objectives forms a system. Basically, there are three major components in every system, namely input, processing, and output.
In a system, the different components are connected with each other and they are interdependent. For example, the Human body represents a completely natural system. The objective of the system demands that some output is produced as a result of processing the suitable inputs. A well-designed system also includes an additional element referred to as ‘control’ that provides feedback to achieve desired objectives of the system.
Definition of System Analysis
Below that, we have explained the definition of system analysis:
System analysis is the process of collecting factual data, understanding the processes involved, identifying problems, and recommending feasible suggestions for improving the system’s functioning.
This involves studying the business processes, gathering operational data, understanding the information flow, finding out bottlenecks, and evolving solutions for overcoming the weaknesses of the systems to achieve the organizational goals.
System analysis also includes subdividing a complex process involving the entire system, identification of data stores, and manual processes.
The major objectives of systems analysis are to find answers for each business process:
- What is being done?
- How is it being done?
- Who is doing it?
- When is he doing it?
- Why is it being done?
- How can it be improved?
It is more of a thinking process and involves the creative skills of the System Analyst. It attempts to give birth to a new, efficient system that satisfies the current needs of the user and has scope for future growth within the organizational constraints.
The result of this process is a logical system design. Systems analysis is an iterative process that continues until a preferred and acceptable solution emerges.
What is Subsystem?
A Complex system is difficult to comprehend when considered as a whole. Therefore, the system is decomposed or factored into subsystems. A subsystem is part of a larger system. Each system is divided into subsystems, which in turn are made up of subsystems, each sub-system being delineated by its boundaries.
The interconnections and interactions between the subsystems are termed interfaces that occur at the boundary and take the form of inputs and outputs.
The boundaries and interfaces are defined, so that the sum of the subsystems constitutes the entire system. This process of decomposition is continued with subsystems divided into smaller subsystems until the smallest subsystem is of manageable size. The subsystems resulting from this process generally form hierarchical structures.
Decomposition into subsystems is used to analyze an existing system and to design and implement a new system. In both cases, the investigator or designer how to factor, i.e. where to draw the boundaries. The decisions will depend on the objectives of the decomposition and also on individual differences among designers, the latest should be minimized.
Black Box System
The transformation process in certain sub-systems, especially at the lowest level, may not be defined. However, the inputs and outputs are known. Such a sub-system is called a black box system.
Characteristics of System
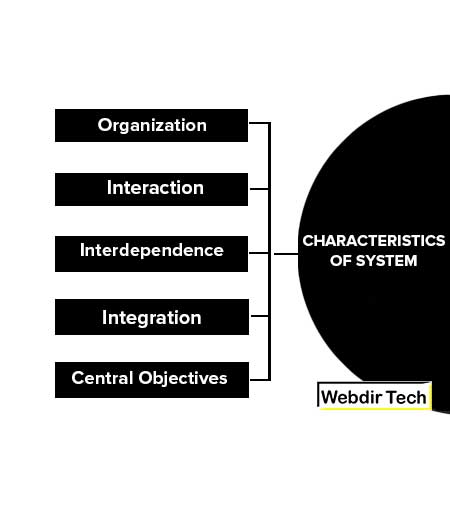
These are the characteristics of system explained below:
- Organization
- Interaction
- Interdependence
- Integration
- Central Objectives
Organization
Organization implies structure and order. It can also be defined as the arrangement of components that helps to achieve objectives.
For Example: In the design of a business system, the hierarchical relationships starting with the president on top and leading toward the workers represent the organization structure. So this gives the authority structure and specifies the formal flow of communication. Likewise, a computer system is designed around an input device, a central processing unit, an output device, and one or more storage units.
Interaction
Interaction refers to the manner in which each component functions with other components of the system. ie, there should be an interrelationship between each component of a system.
For Example: In an organization, there should be an interaction between the purchasing department and production department, the same way advertising with sales, and payroll with personnel.
In a computer system, the central processing unit must interact with the input device to solve a problem. In turn, the main memory holds programs and data that the arithmetic unit uses for computation.
Interdependence
This is one of the important characteristics of a system. Interdependence means the parts or components of an organization or computer system depend on one another. Each component or part should depend on other components of an organization.
One component or subsystem depends on the input of another subsystem for proper functioning, ie, the output of one subsystem is the required input for another subsystem.
For Example: A decision to computerize an application is initiated by the user, analyzed and designed by the analyst, and programmed and tested by the computer operator. In the below figure: none of these persons can perform properly without the required input from others in the computer center subsystem.
Integration
Integration refers to the holism of systems. Synthesis follows the analysis of the central objective of the organization. It is concerned with how a system is tied together. It is more than sharing a physical part or location. Likewise, it means that parts of the system work together within the system, even though each part performs a unique function.
Central Objectives
The last characteristic of a system is its central objective. Objectives may be real or stated. The important point is that users must know the central objective of a computer application early in the analysis for a successful design and conversion.
FAQ Related to the System Concept
What is the meaning of system concept?
A collection of components that work together to realize some objectives forms a system. There are three major components in every system, namely input, processing, and output.
What are the characteristics of system concepts?
The following are the characteristics of system concepts:
1. Environment and Boundaries
2. Natural and Human-Made Systems
3. Theoretical Framework
4. Process and Transformation Process
5. Subsystem
6. System Model
7. System Architecture.
What are the characteristics of system?
The following are the characteristics of system:
1. Organization
2. Interaction
3. Interdependence
4. Integration
5. Central Objectives.
