What is Computer System?
A computer system primarily comprises a central processing unit (CPU), memory, input/output devices, and storage devices. All these components function together as a single unit to deliver the desired output. A computer system comes in various forms and sizes.
It can vary from a high-end server to a personal desktop, laptop, tablet computer, or smartphone.
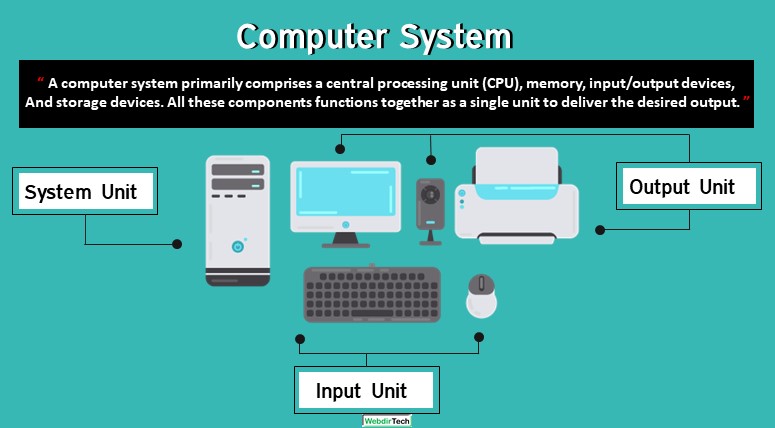
Computer System Definition
[su_quote cite=””]A computer system is a set of integrated devices that are central processing unit (CPU), memory, input/output devices, and storage devices. All these components function together as a single unit to deliver the desired output.[/su_quote]
Computer Definition
[su_quote cite=””]A computer is an electronic device that accepts user input (data) and processes it under the influence of a set of instructions referred to as programs to produce the desired output.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=””]A computer is an electronic device, operating under the control of instructions stored in its own memory. These instructions tell the machine what to do. The computer is capable of accepting data (input), processing data arithmetically and logically, producing output from the processing, and storing the results for future use. Most computers that sit on a desktop are called Personal Computers (PCs).[/su_quote]
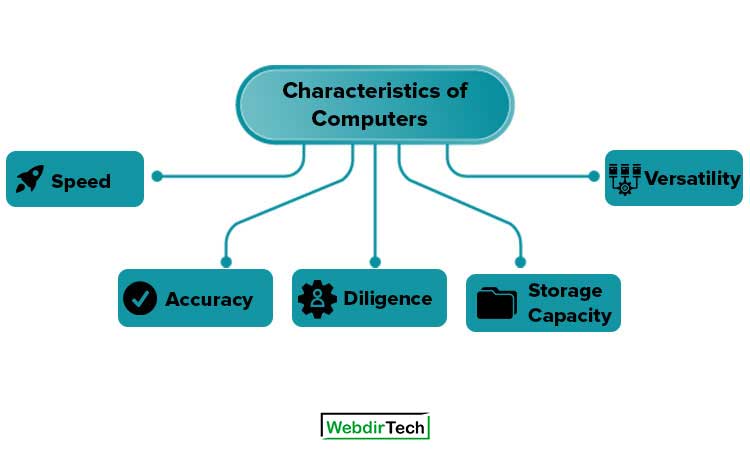
Characteristics of Computers
The characteristics of computers that have made them so powerful and universally useful. Let us discuss them briefly:
- Speed
- Accuracy
- Diligence
- Versatility
- Storage Capacity
Speed
Computers work at an incredible speed. A powerful computer is capable of performing about 3-4 million simple instructions per second.
Accuracy
In addition to being fast, computers are also accurate. Errors that may occur can almost always be attributed to human error (inaccurate data, poorly designed systems,s or faulty instructions/programs written by the programmer).
Diligence
Unlike human beings, computers are highly consistent. They do not suffer from human traits of boredom and tiredness resulting in a lack of concentration. Therefore, computers are better than humans in performing voluminous and repetitive jobs.
Versatility
Computers are versatile machines and are capable of performing any task as long as it can be broken down into a series of logical steps. The presence of computers can be seen in almost every sphere – Railway/Air reservations, Banks, Hotels, Weather forecasting and many more.
Storage Capacity
Today’s computers can store large volumes of data. A piece of information once recorded (or stored) in the computer, can never be forgotten and can be retrieved almost instantaneously.
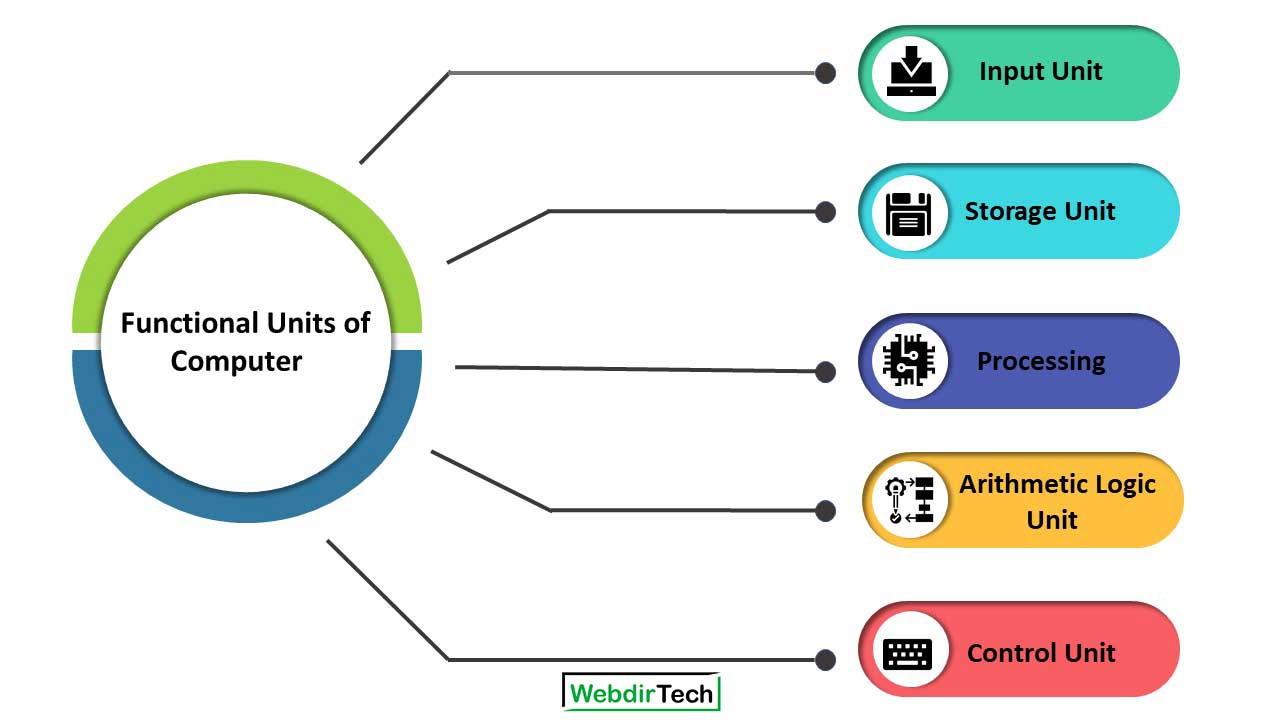
Functional Units of Computer
These are the functional units of computer let us discuss them briefly:
- Input Unit
- Storage Unit
- Processing
- Arithmetic Logic Unit
- Control Unit
Input Unit
This unit is used for entering data and programs into the computer system by the user for processing.
Storage Unit
The storage unit is used for storing data and instructions before and after processing.
Processing
The task of performing operations like arithmetic and logical operations is called processing. The Central Processing Unit (CPU) takes data and instructions from the storage unit and makes all sorts of calculations based on the instructions given and the type of data provided.
It is then sent back to the storage unit. CPU includes an Arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and a control unit (CU).
Arithmetic Logic Unit
All calculations and comparisons, based on the instructions provided, are carried out within the ALU. It performs arithmetic functions like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, and also logical operations like greater than, less than, and equal to, etc.
Control Unit
Controlling of all operations like input, processing, and output are performed by the control unit. It takes care of step-by-step processing of all operations inside the computer.
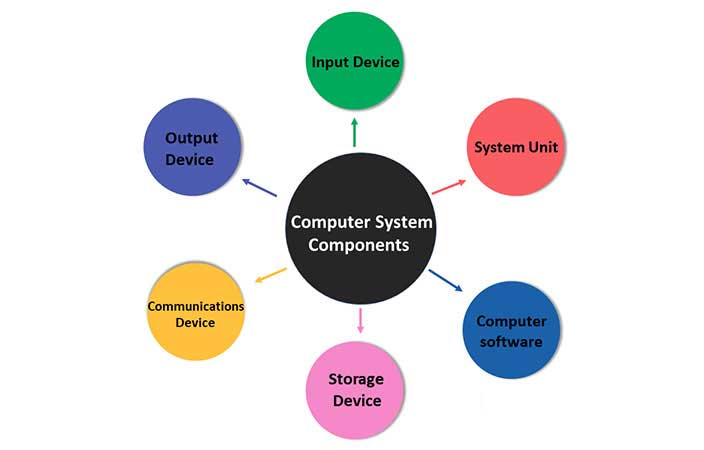
Computer System Components
These are the computer system components let us discuss them briefly:
- Input Device
- Output Device
- System Unit
- Computer software
- Storage Device
- Communications Device
Input Device
The devices through which control signals are sent to a computer are termed input devices. These devices convert the input data into a digital form that is acceptable by the computer system.
Some examples of input devices include the keyboard, mouse, scanner, touch screen, Light pen, Joystick, Optical Scanner, Microphone, Modem, Magnetic ink character recognition (MICR), Optical mark recognition (OMR), Bar code reader, etc.
Output Device
Output devices consist of hardware that transfers information from the computers CPU to the computer user. This includes the monitor, Printer, plotters, or speaker.
System Unit
The system unit is a case that contains electronic components of the computer used to process data. The inside of the system unit on a desktop personal computer includes:
- Motherboard
- Processor (CPU)
- Memory
- Computer software
Motherboard: The motherboard is a printed circuit board that connects other components through the use of traces or electrical pathways. The motherboard is indispensable to the computer and provides the main computing capability. Personal computers normally have one central processing unit (CPU) on the motherboard.
Processor (CPU): It is the electronic circuitry of a computer that carries out the actual processing and is usually referred to as the brain of the computer. It is commonly called a processor also. Physically, a CPU can be placed on one or more microchips called integrated circuits (IC). The ICs comprise semiconductor materials.
The CPU is given instructions and data through programs. The CPU then fetches the program and data from the memory and performs arithmetic and logic operations as per the given instructions and stores the result back to memory.
While processing, the CPU stores the data, as well as for instructions in its local memory, called registers. Registers are part of the CPU chip and are limited in size and number. Different registers are used for storing data, instructions, or intermediate results.
The CPU has two main components: The arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) and Control Unit (CU)
ALU performs all the arithmetic and logic operations that need to be done as per the instruction in a program.
CU controls sequential instruction execution, interprets instructions, and guides data flow through the computer’s memory, ALU, and input or output devices. CPU is also popularly known as a microprocessor.
Memory: A computer system needs memory to store the data and instructions for processing. Whenever we talk about the ‘memory of a computer system, we usually talk about the main or primary memory. The secondary memory (also called storage device) is used to store data, instructions and results permanently for future use.
Computer memory can be classified into two types; primary memory and secondary memory.
- RAM or Random Access Memory
- ROM or Read Only Memory
RAM or Random Access Memory is the unit in a computer system. It is the place in a computer where the operating system, application programs, and the data in current use are kept temporarily so that they can be accessed by the computer’s processor. It is said to be ‘volatile’ since its contents are accessible only as long as the computer is on. The contents of RAM are no more available once the computer is turned off.
ROM or Read Only Memory is a special type of memory that can only be read and contents of which are not lost even when the computer is switched off. It typically contains the manufacturer’s instructions. Among other things, ROM also stores an initial program called the ‘bootstrap loader’ whose function is to start the operation of the computer system once the power is turned on.
Computer Software
Computer software is a set of programs, procedures, code, and related data that provide the instructions for telling computer hardware what to do and types of computer software can be divided into two general categories:
- System Software (Operating systems)
- Application Software
System Software: System software is any computer software that manages and controls computer hardware so that application software can perform a task. Operating systems, such as Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X, or Linux, are prominent examples of system software.
Application Software: Application Software is a program that enables the end-user to perform specific, productive tasks, such as MS Word for word processing or Photoshop for image manipulation.
Storage Device
Storage devices provide permanent storage of information and programs for retrieval by the computer. The two main types of storage devices are disk drives and memory. There are several types of disk drives:
- Hard Disk
- Floppy Disk
- Magneto-Optical Disc Drives
- Compact Disc Drives
- Digital Video Disc (DVD)
- Flash Drives
- Memory Cards
Hard disk: Hard Disk drives store information in magnetic particles embedded in a disk. Usually a permanent part of the computer, hard disk drives can store large amounts of information and retrieve that information very quickly. The disks are of different sizes such as 1G, 10G, 40G, etc.
Floppy Disk: Floppy disk drives also store information in magnetic particles embedded in removable disks. Floppy disks store less information than a hard disk drive and retrieve the information at a much slower rate.
Magneto-Optical Disc Drives: Magneto-optical disc drives store information on removable discs that are sensitive to both laser light and magnetic fields. They can typically store as much information as hard disks, but they have slightly slower retrieval speeds.
Compact Disc Drives: Compact Disc Drives store information on pits burned into the surface of a disc of reflective material such as CD-ROM. CD-ROMs can store about as much information as a hard drive but have a slower rate of information retrieval.
Digital Video Disc (DVD): This is similar and works like a CD-ROM but can store more than 15 times as much information.
Flash Drives: Flash drives work as floppy disks but are more sensitive than hard disks that must be ejected logically before final removal from the computer system. It has more memory than floppy disks.
Memory Cards: Memory Cards work as flash drives but with an additional device called the card reader. This is very effective and more durable than flash drives.
Some devices serve more than one purpose. For example, floppy disks may also be used as input devices if they contain information to be used and processed by the computer user. In addition, they can be used as output devices if the user wants to store the results of computations on them.
Communications Device
A communications device is any type of hardware capable of transmitting data, instructions, and information between a sending device and a receiving device. One type of communications device that connects a communications channel to a sending or receiving device such as a computer is a modem.
Computers process data as digital signals. Data, instructions, and information travel along a communications channel in either analog or digital form depending on the communications channel. An analog signal consists of a continuous electrical wave. A digital signal consists of individual electrical pulses that represent bits grouped together into bytes.
Types of Communications Devices: Dial-up Modems, ISDN and DSL modems, Cable Modems, Wireless Modems, Network Cards, Wireless Access Points, and Routers.
FAQ About Computer System
What is computer system short definition?
A computer system primarily comprises a central processing unit (CPU), memory, input/output devices, and storage devices. All these components function together as a single unit to deliver the desired output. A computer system comes in various forms and sizes.
What is system software in simple words?
Computer software is a set of programs, procedures, code, and related data that provide instructions for telling computer hardware what to do and how to do it Software is broadly divided into two types:
1. System Software (Operating systems)
2. Application Software
What is system unit in computer?
The system unit is a case that contains electronic components of the computer used to process data. The inside of the system unit on a desktop personal computer includes:
1. Motherboard
2. Processor (CPU)
3. Memory
4. Computer software
What are the four components of a computer system?
These are the computer system components mentioned below:
1. Input Device
2. Output Device
3. System Unit
4. Computer software
5. Storage Device
6. Communications Device
What are the characteristics and capabilities of computers?
The characteristics of computers that have made them so powerful and universally useful are:
1. Speed
2. Accuracy
3. Diligence
4. Versatility
5. Storage Capacity
